Baseball is a beloved sport that combines athleticism, strategy, and teamwork. However, like any physical activity, it comes with its fair share of risks.
Baseball injuries can range from minor sprains to more serious conditions that require medical attention.
In this blog post, we will explore the ten most common baseball injuries, providing insights into their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures.
Whether you’re a player, coach, or a concerned parent, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the risks associated with the sport and how to minimize them. So, let’s get started.
10 Most Common Baseball Injuries Commonly Happen
Here are the 10 most common baseball injuries alongside the symptoms, medication, and prevention.
1. Torn Labrum

Source: jsonline.com
A torn labrum is a common injury among baseball players, particularly pitchers. The labrum refers to the cartilage that surrounds the shoulder socket, providing stability to the joint. Repetitive overhead throwing motions can lead to a tear in the labrum, causing pain, instability, and a limited range of motion in the shoulder joint.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a torn labrum is shoulder pain, which can be sharp or aching in nature. Individuals may also experience a popping or clicking sensation in the shoulder, weakness, decreased range of motion, and difficulty in throwing or lifting objects.
Medication
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used for pain management and to reduce inflammation. Corticosteroid injections may also be administered to alleviate pain and inflammation.
In some cases, if conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary to repair the torn labrum.
Prevention
Preventing a torn labrum involves maintaining proper pitching mechanics, which includes using correct arm and shoulder positioning during the throwing motion. It is essential to follow proper training and conditioning programs, focusing on strengthening the shoulder and rotator cuff muscles.
Gradual progression of throwing intensity and listening to the body’s signals of fatigue or pain can also help prevent this injury.
2. Tendonitis
Source: espn.in
Tendonitis refers to inflammation of a tendon, commonly affecting the elbow, shoulder, or wrist in baseball players. Overuse and repetitive motions put stress on the tendons, leading to inflammation and pain.
Symptoms
Symptoms of tendonitis include pain, swelling, tenderness, limited range of motion, and difficulty in gripping or throwing. The pain is usually localized to the affected tendon.
Medication
NSAIDs are often used to manage pain and reduce inflammation associated with tendonitis. Corticosteroid injections may be administered to provide temporary relief. Physical therapy is also commonly recommended to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected tendon and promote healing.
Prevention
Preventing tendonitis involves gradually increasing training intensity to allow the tendons to adapt to the stress. Proper warm-up and cool-down routines are essential to prepare the muscles and tendons for activity and aid in recovery.
Maintaining good throwing mechanics and technique can also reduce the risk of tendonitis. Regular strengthening exercises, particularly focused on the muscles around the joint involved, help to provide stability and support.
3. Rotator Cuff Injuries

Rotator cuff injuries are prevalent in baseball players, particularly pitchers, and refer to damage or tears in the muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. These injuries often occur due to repetitive overhead motions and can cause pain, weakness, and limited mobility in the shoulder.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a rotator cuff injury include shoulder pain, weakness, difficulty in lifting or reaching, popping or clicking sounds, and limited range of motion. Pain is typically felt deep within the shoulder and may radiate down the arm.
Medication
NSAIDs are commonly used for pain management and to reduce inflammation. Corticosteroid injections may be administered to provide temporary relief. Physical therapy is an integral part of the treatment, focusing on strengthening the rotator cuff muscles and improving shoulder stability.
In severe cases, where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the torn tendons.
Prevention
Preventing rotator cuff injuries involves regular strengthening exercises for the rotator cuff and shoulder muscles. This helps to provide stability to the shoulder joint and better withstand the stress placed on it during throwing.
It is crucial to maintain proper throwing mechanics, including proper arm and shoulder positioning. Gradually increasing throwing intensity and listening to the body’s signals of fatigue or pain are also important in injury prevention.
4. Dead Arm

Dead arm syndrome is characterized by a temporary loss of strength and velocity in the throwing arm, typically experienced by pitchers. It can be caused by fatigue, overuse, or poor mechanics.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of a dead arm is a noticeable decrease in throwing velocity. Pitchers may also experience pain or discomfort and have difficulty achieving accurate pitches.
Medication
The main treatment for a dead arm is rest. Allowing the arm to recover and regain its strength is crucial. Physical therapy may be recommended to address any underlying muscle imbalances or mechanical issues that may contribute to the condition.
Prevention
Preventing a dead arm involves proper conditioning and strengthening of the shoulder and arm muscles. Gradually increasing throwing intensity and volume allows the arm to adapt and reduces the risk of overuse injuries.
Regular rest and recovery periods are essential to give the arm time to recuperate. Maintaining good throwing mechanics and avoiding excessive throwing when fatigued is also important in preventing a dead arm.
5. Ankle Sprain
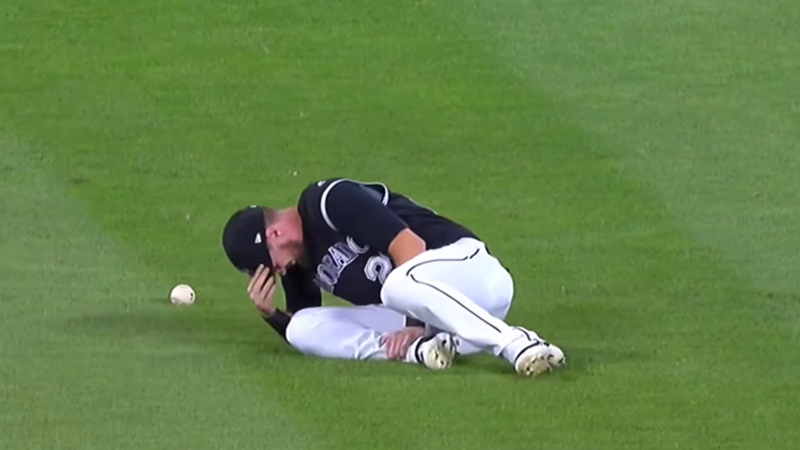

Ankle sprains are common in baseball, particularly during running, sliding, or fielding activities. They occur when the ligaments supporting the ankle joint are stretched or torn.
Symptoms
Symptoms of an ankle sprain include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected ankle. Instability and a feeling of the ankle “giving way” may also be present.
Medication
The standard treatment for an ankle sprain is the RICE protocol, which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. NSAIDs may be used to manage pain and inflammation.
Ankle braces or supports can provide stability during the healing process. Physical therapy may be recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and stability to the ankle.
Prevention
Preventing ankle sprains involves wearing supportive footwear with proper ankle support. Performing ankle strengthening exercises, particularly focusing on the muscles around the ankle joint, helps to provide stability.
Proper warm-up and stretching routines are essential to prepare the ankle for activity. Avoiding uneven or slippery surfaces and being mindful of running mechanics can also reduce the risk of ankle sprains.
6. Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Injury
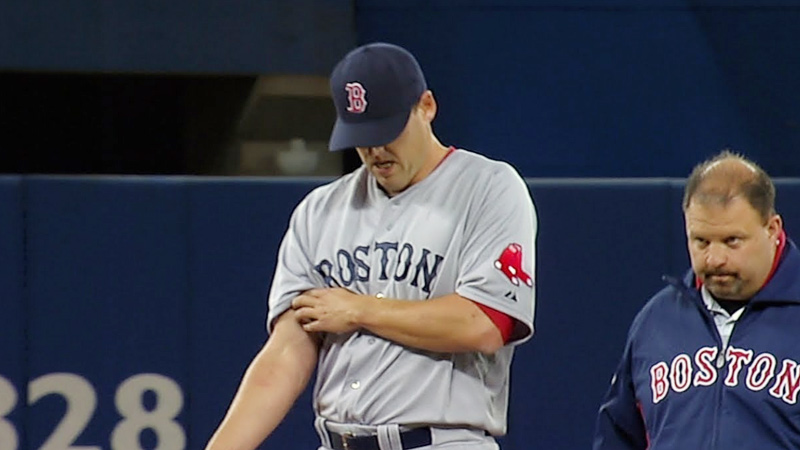

UCL injuries, often referred to as “Tommy John” injuries, occur when the ulnar collateral ligament in the elbow is stretched or torn. These injuries are prevalent among pitchers due to the stress placed on the ligament during the throwing motion.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a UCL injury is pain on the inside of the elbow. Pitchers may experience decreased throwing accuracy and a feeling of instability in the elbow.
Medication
Treatment options for UCL injuries range from conservative management to surgical intervention. Rest and physical therapy may be sufficient for partial tears or low-grade injuries.
NSAIDs are commonly used for pain management. In severe cases, where the UCL is completely torn or conservative treatments fail, surgical repair or reconstruction (Tommy John surgery) may be necessary.
Prevention
Preventing UCL injuries involves gradually increasing throwing intensity and volume to allow the ligament to adapt. Maintaining proper throwing mechanics, including proper arm and elbow positioning, is crucial.
Regular conditioning and strengthening exercises for the forearm and elbow muscles help provide stability and support. Monitoring pitch counts and listening to the body’s signals of fatigue or pain is also important in preventing UCL injuries.
7. Wrist Tendonitis
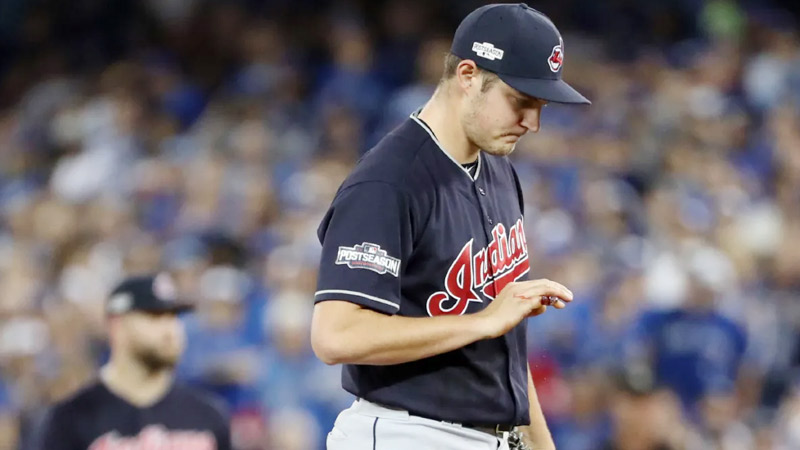

Source: thestar.com
Wrist tendonitis refers to inflammation of the tendons in the wrist, commonly caused by repetitive motions such as batting or throwing.
Symptoms
Symptoms of wrist tendonitis include pain, swelling, and difficulty gripping or moving the wrist. The pain is usually localized to the affected tendon.
Medication
Treatment for wrist tendonitis involves rest, reducing or modifying activities that exacerbate symptoms, and the use of NSAIDs for pain relief and inflammation reduction.
Immobilizing the wrist with a brace or splint may be necessary in severe cases. Physical therapy is often recommended to strengthen the muscles around the wrist, improve flexibility, and promote healing.
Prevention
Preventing wrist tendonitis includes proper warm-up and stretching routines to prepare the muscles and tendons for activity. Gradually increasing the intensity of batting or throwing sessions allows the wrist to adapt to the stress.
Using proper technique and mechanics when performing wrist-intensive movements helps to minimize strain on the tendons. Regular conditioning exercises for the forearm and wrist muscles also contribute to prevention.
8. Oblique Strains
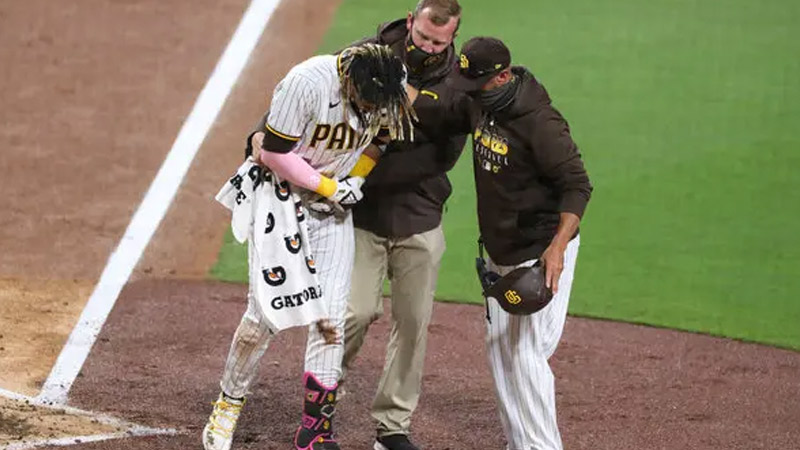

Source: nytimes.com
Oblique strains occur when the muscles or tendons in the abdominal area are stretched or torn. They can be caused by rotational movements during batting, throwing, or running.
Symptoms
Symptoms of an oblique strain include pain, tenderness, and difficulty with twisting or bending motions. Activities that involve rotation or exertion of the abdominal muscles may exacerbate the pain.
Medication
Treatment for oblique strains typically involves rest, allowing the injured muscle to heal. The RICE protocol is commonly used, along with NSAIDs for pain management. Physical therapy may be recommended to facilitate healing, restore flexibility and strength, and prevent future strains.
Prevention
Preventing oblique strains involves regular core strengthening exercises to provide stability to the abdominal muscles. Gradual progression in training intensity and volume allows the muscles to adapt and reduces the risk of strain.
Proper warm-up routines that incorporate rotational movements prepare the muscles for activity.
Avoiding sudden or excessive twisting motions and maintaining proper technique during rotational activities are also important preventive measures.
9. Pitcher’s Elbow
Source: post-gazette.com
Pitcher’s elbow refers to a variety of elbow injuries common among pitchers. It can include conditions such as medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow), osteochondritis dissecans, or stress fractures.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a pitcher’s elbow can include pain on the inside or outside of the elbow, decreased throwing velocity, limited range of motion, and difficulty with gripping or throwing.
Medication
Treatment for a pitcher’s elbow depends on the specific injury involved. Rest, physical therapy, and NSAIDs may be used for mild cases. Corticosteroid injections may provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Severe cases or injuries that fail to respond to conservative treatment may require surgical intervention.
Prevention
Preventing a pitcher’s elbow involves proper conditioning and strengthening of the forearm and elbow muscles.
Gradually increasing throwing intensity and volume, along with monitoring pitch counts, help reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
Maintaining good throwing mechanics and technique, including proper arm and elbow positioning, is crucial. Regular rest and recovery periods allow the body to recuperate and prevent overuse injuries.
10. Knee Injuries or Tears
Source: completegamept.com
Knee injuries in baseball players can range from sprains and strains to more severe ligament tears, such as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or meniscus tears. These injuries can occur during running, sliding, or fielding activities.
Symptoms
Symptoms of knee injuries or tears include pain, swelling, instability, and difficulty with weight-bearing or range of motion. There may be a sensation of the knee “giving way” or locking.
Medication
Treatment for knee injuries depends on the specific injury involved. The RICE protocol, along with NSAIDs, is typically used for pain management and to reduce inflammation.
Knee braces or supports may be recommended to provide stability during the healing process.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in strengthening the knee, improving flexibility, and restoring function. Severe cases or injuries that fail to respond to conservative treatment may require surgical intervention.
Prevention
Preventing knee injuries or tears involves proper warm-up and stretching routines to prepare the knee and surrounding muscles for activity.
Regular conditioning exercises for the lower body, with a focus on strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles, help to provide stability and support.
Wearing supportive footwear and being mindful of running mechanics and fielding techniques can also reduce the risk of knee injuries. Avoiding excessive stress on the knees and listening to the body’s signals of pain or fatigue are important preventive measures.
FAQs
What are the most common baseball injuries?
Baseball players often encounter injuries such as rotator cuff tears, elbow ligament sprains (Tommy John injury), muscle strains, fractures, concussions, ankle sprains, and hamstring strains, among others. This article will delve into each injury in detail.
What causes these injuries?
Baseball injuries can occur due to a variety of factors, including overuse, poor conditioning, inadequate warm-up, improper throwing mechanics, collisions, repetitive stress, and sudden impacts. Understanding the causes can aid in injury prevention.
How can players prevent baseball injuries?
Preventive measures play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of baseball injuries. These include proper warm-up and stretching routines, strength and conditioning exercises, using appropriate protective gear, maintaining good pitching mechanics, resting and recovering adequately, and practicing good sportsmanship.
What are the symptoms of common baseball injuries?
Each injury presents unique symptoms. For example, rotator cuff tears may cause shoulder pain, weakness, and limited range of motion, while Tommy John injuries can result in elbow pain, swelling, and difficulty throwing. Recognizing the symptoms is essential for early intervention and treatment.
How can coaches and parents contribute to injury prevention?
Coaches and parents have a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of baseball players.
By promoting proper training techniques, enforcing rest and recovery periods, advocating for appropriate protective equipment, and educating players about injury prevention strategies, they can greatly reduce the risk of injuries.
Conclusion
Baseball injuries are an unfortunate reality of the sport, but by understanding their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, players, coaches, and parents can work together to minimize the risks.
This blog post has provided an overview of the ten most common baseball injuries, offering insights into their prevention and management.
By prioritizing safety, proper training, and a culture of injury prevention, we can continue to enjoy the game of baseball while keeping players safe and healthy on and off the field. Good luck.







