Michael Jordan, the iconic basketball legend, is celebrated for his unparalleled skills on the court.
However, what often remains hidden beneath his dunks, game-winning shots, and championship titles is his considerable physical strength.
Jordan’s max bench press, a measure of his upper-body strength, stood at approximately 300 pounds (136 kilograms) during his prime.
This remarkable feat set him apart from his NBA peers and rivals, considering his primary focus was on speed, agility, and endurance rather than pure strength.
In this article, we delve into the intriguing facets of Michael Jordan’s bench press prowess and how it contributed to his legendary status in the world of sports.
About Michael Jordan
Michael Jordan, often referred to as “MJ” or “His Airness,” is widely regarded as one of the greatest basketball players in the history of the sport.
Here are some key details and highlights about Michael Jordan:
Early Life and College Career
Michael Jeffrey Jordan was born on February 17, 1963, in Brooklyn, New York. He played college basketball for the University of North Carolina, where he won the NCAA championship in 1982.
NBA Career
Jordan was selected by the Chicago Bulls as the third overall pick in the 1984 NBA Draft. He played the majority of his career with the Bulls, but he also had a brief retirement and stint with the Washington Wizards. He is known for his scoring ability, athleticism, and competitive spirit.
Championships and Achievements

Jordan led the Chicago Bulls to six NBA championships in the 1990s, earning numerous accolades, including five NBA Most Valuable Player (MVP) awards. He was a 14-time NBA All-Star, a 10-time scoring champion, and a 10-time All-NBA Team selection.
Air Jordan
Michael Jordan’s association with Nike led to the creation of the iconic Air Jordan line of basketball shoes, which remains popular and influential in the world of sports and fashion.
Olympic Success
Jordan was a key member of the U.S. men’s basketball team, known as the “Dream Team,” which won the gold medal at the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona. He also won gold medals with Team USA in 1984 and 1992.
Retirement and Comeback
Jordan retired from basketball for the first time in 1993 but returned to the NBA in 1995. He retired a second time in 1999 and then made a brief comeback with the Washington Wizards in 2001 before retiring for good in 2003.
Impact and Legacy
Michael Jordan’s influence on the game of basketball, sports culture, and popular culture is immense.
He is often cited as an example of dedication, work ethic, and competitiveness. His impact extends far beyond the basketball court, as he remains a global icon.
Business Ventures
Jordan has been successful in various business ventures, including ownership of the Charlotte Hornets, an NBA team.
He is also involved in the fashion and sneaker industry and has numerous endorsements and investments.
Hall of Fame
Michael Jordan was inducted into the Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame in 2009, recognizing his incredible contributions to the sport.
Personal Life
Jordan’s personal life has been relatively private, but he is known for his philanthropic efforts and contributions to various charitable causes.
What Was Michael Jordan’s Max Bench Press?
Michael Jordan, widely regarded as one of the greatest basketball players of all time, had a maximum bench press of around 300 pounds (136 kilograms) at his peak.
This feat is especially impressive considering that Jordan was primarily known for his skills in speed, agility, and endurance on the basketball court, rather than for his pure physical strength.
In the world of professional basketball, where many players focus more on their athletic abilities and basketball skills, weightlifting and strength training often take a backseat.
The average NBA player’s bench press typically hovers around 185 pounds (84 kilograms) for a single repetition.
Michael Jordan’s bench press was notably higher than that of his peers and rivals during his time in the NBA, including legendary players like Magic Johnson, Larry Bird, and Kobe Bryant.
While Jordan’s strength was notable for a basketball player, he was still outmatched by some of the NBA’s most powerful athletes, such as Shaquille O’Neal, Dwight Howard, and LeBron James, who could bench press significantly more weight.
Even beyond the basketball court, Jordan’s bench press performance was remarkable for a celebrity.
When compared to other well-known figures in Hollywood, his strength was on par with actors like Michael B. Jordan, Chris Hemsworth, and Hugh Jackman, who are known for their muscular physiques.
However, it’s essential to note that Jordan’s bench press numbers were still far behind some of the strongest celebrities in Hollywood, including Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson, John Cena, and Arnold Schwarzenegger, who had notably higher bench press figures.
What Is Bench Press Good For?
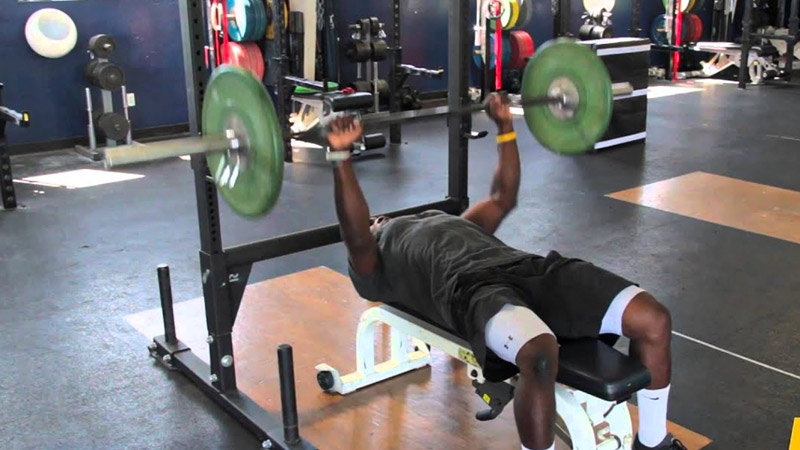

The bench press is a fundamental and versatile strength-training exercise that offers a wide range of benefits for individuals looking to improve their physical fitness and athletic performance.
Here are some of the key advantages of including the bench press in your workout routine:
Upper Body Strength
The bench press primarily targets the muscles of the chest, shoulders, and triceps. It helps to develop upper body strength, which is essential for various activities in daily life, sports, and fitness.
Muscle Hypertrophy
Performing the bench press with progressively heavier weights can lead to muscle growth in the chest, shoulders, and triceps, contributing to a more muscular and defined upper body.
Improved Pushing Power
Bench pressing is particularly beneficial for enhancing your pushing strength, which can translate into improved performance in activities like pushing open heavy doors, shoving objects, and pushing opponents in contact sports.
Enhanced Athletic Performance
Many sports, including football, basketball, and martial arts, involve pushing or blocking opponents. A strong chest and upper body can be a significant advantage in these activities.
Bone Health
Weight-bearing exercises like the bench press can contribute to improved bone density, helping to reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Injury Prevention
Strengthening the muscles around the shoulder joint, which is crucial for the bench press, can help reduce the risk of shoulder injuries and improve stability in that area.
Improved Posture
A well-balanced upper body, which includes a strong chest, can aid in maintaining good posture and reducing the risk of musculoskeletal issues.
Metabolism and Fat Loss
Resistance training, such as the bench press, can help increase your metabolism and contribute to fat loss by building lean muscle mass, which burns more calories at rest.
Mental Strength
The bench press, like other strength-training exercises, requires mental focus and determination. It can help improve mental resilience and discipline.
Overall Fitness
Incorporating the bench press into a comprehensive workout routine contributes to overall fitness and well-rounded strength development.
Is Bench Press for Chest or Abs?
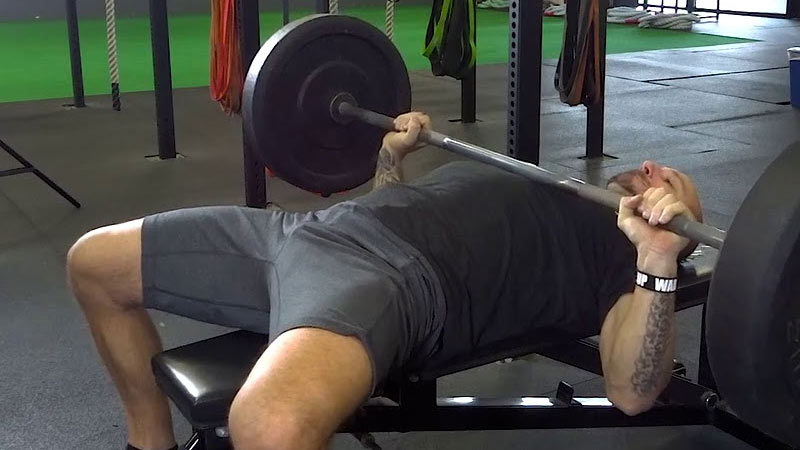

The bench press primarily targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps, not the abs. It’s a compound exercise that involves pressing a weight (usually a barbell or dumbbells) away from your chest.
The main muscles worked during the bench press include:
- Pectoralis Major: This is the primary chest muscle worked during the bench press. It’s responsible for the horizontal adduction of the shoulder joint, which means it brings your upper arms closer to the midline of your body.
- Anterior Deltoids: These are the front shoulder muscles, and they assist in the pressing motion during the bench press.
- Triceps Brachii: The triceps, located on the back of the upper arm, are responsible for extending the elbow during the bench press.
Does Bench Press Work All Chest?
The bench press primarily targets the pectoralis major, the large chest muscle, but it doesn’t work all parts of the chest equally. It primarily engages the central or middle portion of the chest.
The degree to which different parts of the chest are worked depends on factors like grip width and barbell path.
Here’s a breakdown:
- Upper Chest: To emphasize the upper chest, you can adjust your bench press technique by using an incline bench or an incline on a bench press machine. Incline bench presses angle the bench at about 30-45 degrees, shifting more of the workload to the upper chest.
- Lower Chest: To target the lower chest, decline bench presses can be used. A decline bench is angled downward, which places more stress on the lower part of the chest.
- Middle Chest: The standard flat bench press predominantly targets the middle or central part of the chest.
Will Bench Press Make Arms Bigger?
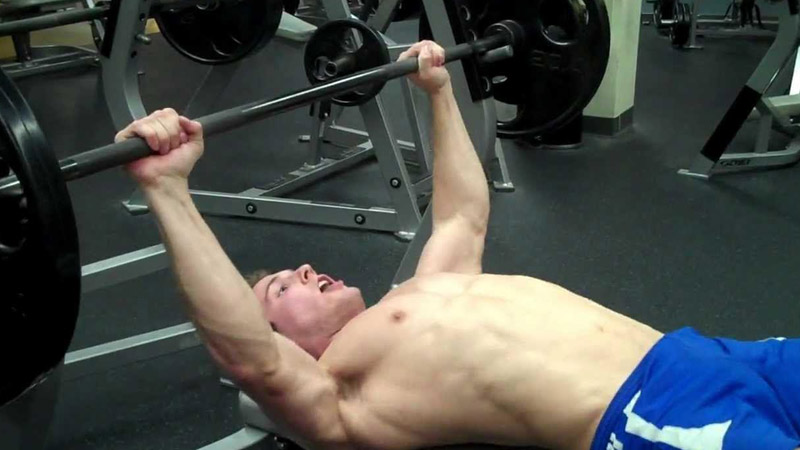

Yes, the bench press can contribute to making your arms, particularly the triceps, bigger and stronger.
While the primary focus of the bench press is on the chest, it’s a compound exercise that also heavily involves the triceps muscles.
Here’s how the bench press can help in building larger and stronger arms:
Triceps Engagement
The triceps, located on the back of your upper arms, are responsible for extending the elbow. When you push the weight during a bench press, the triceps play a significant role in the extension of your arms.
As you progressively increase the weight or resistance in your bench press, your triceps will get stronger and more developed, leading to increased arm size.
Secondary Bicep Involvement
While the primary muscle worked during the bench press is the triceps, the biceps, located on the front of your upper arms, also play a role in stabilizing the elbow joint during the exercise. Although the biceps are not the primary movers, they are engaged as stabilizers.
Overall Upper Body Strength
A stronger chest and shoulders, which are targeted during the bench press, can also indirectly contribute to more stability and strength in your arms.
As your chest and shoulder muscles get stronger, you can handle heavier weights in various arm-focused exercises, such as bicep curls and tricep extensions, leading to further arm development.
What Are the Disadvantages of Bench Press?
While the bench press is a popular and effective exercise for developing upper body strength and muscle, it does come with some disadvantages and potential risks, particularly when performed improperly or excessively.
Here are some of the disadvantages and considerations associated with the bench press:
Injury Risk
The bench press can pose a risk of injury, especially if not performed with proper form and technique.
Common injuries include shoulder strain, rotator cuff injuries, and pectoral muscle tears. It’s crucial to use proper form and gradually increase the weight to minimize these risks.
Overdevelopment of the Chest
While the bench press is excellent for developing the chest, excessive focus on this exercise at the expense of other muscle groups can lead to an imbalanced physique. Neglecting other muscle groups can result in poor posture and muscle imbalances.
Lack of Functional Strength
Some critics argue that the bench press primarily develops strength for a specific movement (horizontal pushing) and may not translate well into real-life functional strength and activities.
It’s essential to complement the bench press with a variety of exercises to achieve well-rounded strength.
Limited Range of Motion
The bench press typically involves a fixed range of motion, which can neglect certain muscle fibers.
Variations in exercises, such as dumbbell presses or incline/decline bench presses, can help address this limitation.
Pressure on the Shoulders
For some individuals, the bench press can place excessive strain on the shoulders, which may not be suitable for those with pre-existing shoulder issues or limited range of motion. Proper warm-up and shoulder mobility exercises are crucial in such cases.
Risk of Overtraining
Overtraining, a condition in which you train too frequently or intensely without adequate recovery, can occur when individuals become too focused on a single exercise, such as the bench press. Overtraining can lead to fatigue, injury, and a lack of progress.
Equipment and Spotter Dependency
The bench press typically requires access to specific equipment, such as a barbell, bench, and spotter. If you lack access to this equipment or a reliable spotter, performing the exercise safely becomes challenging.
Inadequate Core Activation
While the bench press engages the core for stability, it does not provide the same level of core activation as other exercises like squats or deadlifts. A strong core is essential for overall functional strength and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much can Michael Jordan bench press?
Michael Jordan’s max bench press was reported to be around 300 pounds at his peak.
What about Stephen Curry’s bench press?
Stephen Curry’s bench press performance is about 185 pounds.
How much can LeBron James bench?
LeBron James can bench press around 225 lbs.
How did Michael Jordan’s bench press contribute to his athletic legacy?
Jordan’s bench press showcased his commitment to physical conditioning, complementing his basketball skills and contributing to his iconic status as one of the greatest athletes in history.
Wrap Up
Michael Jordan’s max bench press of around 300 pounds is a testament to his exceptional athleticism and strength.
While he may not have been the absolute strongest among his peers or in the world of sports and entertainment, his achievement was remarkable, given his primary focus on speed, agility, and endurance as a basketball player.
Jordan’s bench press performance set him apart from many NBA players and showcased his dedication to all facets of his physical conditioning.
It symbolizes his relentless pursuit of excellence, not only on the basketball court but also in the realm of physical fitness, further solidifying his legacy as one of the greatest athletes of all time.







