Basketball is a fast-paced and physically demanding sport that requires agility, strength, and quick movements. However, along with the excitement of the game, injuries are a common occurrence.
From ankle sprains to knee strains and shoulder dislocations, basketball players face a range of potential injuries. In this article, we will explore the most common basketball injuries, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
By understanding these injuries, players can take precautions and seek appropriate care to prevent and manage them effectively. Stay focused.
Some of the Most Common Basketball Injuries
Here we will discuss some of the most common basketball injuries in a brief manner. Check them out below.
Ankle Sprain

Source: ocfeet.com
Ankle sprains are one of the most common basketball injuries due to the frequent changes in direction, pivoting, and jumping involved in the game. They occur when the ligaments surrounding the ankle are overstretched or torn.
Ankle sprains can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of ligament damage. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected ankle.
Proper rehabilitation is crucial for a full recovery, which may involve rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE therapy), strengthening exercises, and physical therapy.
Preventive measures such as wearing supportive basketball shoes, utilizing ankle braces or taping, and practicing proper landing techniques can significantly reduce the risk of future sprains.
Knee Sprain

Source: basketballsocietyonline.com
Knee sprains are often seen in basketball and can involve injuries to different ligaments, including the medial collateral ligament (MCL) or the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
MCL sprains typically occur due to a direct blow to the outside of the knee or sudden changes in direction, while ACL sprains can result from sudden stops, changes in direction, or landing awkwardly.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, instability, and limited range of motion. Treatment varies depending on the severity of the sprain and may involve rest, ice, compression, physical therapy exercises, and in some cases, surgery.
Achilles Tendonitis

Source: cornerstonefootandankle.com
Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury characterized by inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Basketball players are prone to this injury due to the repetitive jumping, acceleration, and deceleration involved in the sport.
Symptoms include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the back of the heel. Treatment typically includes rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medication, stretching, strengthening exercises, and physical therapy. Modifying activity levels and gradually increasing intensity can also help prevent future occurrences.
Patellar Tendinitis

Source: airrosti.com
Patellar tendinitis, commonly known as jumper’s knee, is an overuse injury that affects the tendon connecting the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone. The repetitive jumping and landing actions in basketball can lead to inflammation and degeneration of the patellar tendon.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and tenderness below the kneecap. Treatment usually involves rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy exercises to strengthen the quadriceps and hamstring muscles, and modifying activity levels to allow for adequate healing.
Shin Splints

Source: uhhospitals.org
Shin splints, medically known as medial tibial stress syndrome, refer to pain and inflammation in the front part of the lower leg along the shinbone (tibia).
Basketball players are susceptible to shin splints due to the repetitive stress placed on the shinbone and surrounding muscles from running and jumping. Symptoms include dull or sharp pain along the shin, tenderness, and swelling. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, stretching, and a gradual return to activity after symptoms subside.
Proper footwear, gradual increases in training intensity, and maintaining strong lower leg muscles can help prevent shin splints.
Hamstring Strain

Source: sicscore.com
Hamstring strains are common among basketball players, particularly during explosive movements such as sprinting and jumping. These strains occur when the muscles at the back of the thigh are overstretched or torn.
Symptoms include sudden pain, weakness, tightness, and possible bruising in the back of the leg. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, gentle stretching, and a gradual return to activity.
Physical therapy exercises are beneficial for strengthening the hamstrings and improving flexibility to reduce the risk of future strains.
Groin Strain

Source: silverscreenandroll.com
Groin strains involve the stretching or tearing of the muscles in the groin area, usually caused by sudden movements or changes in direction during basketball.
Symptoms include pain, tenderness, and difficulty moving the leg or performing certain actions like jumping or pivoting.
Treatment includes rest, ice, compression, and physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and stability in the groin muscles. Adequate warm-up, stretching, and strengthening exercises can help prevent groin strains.
Hip Pointer
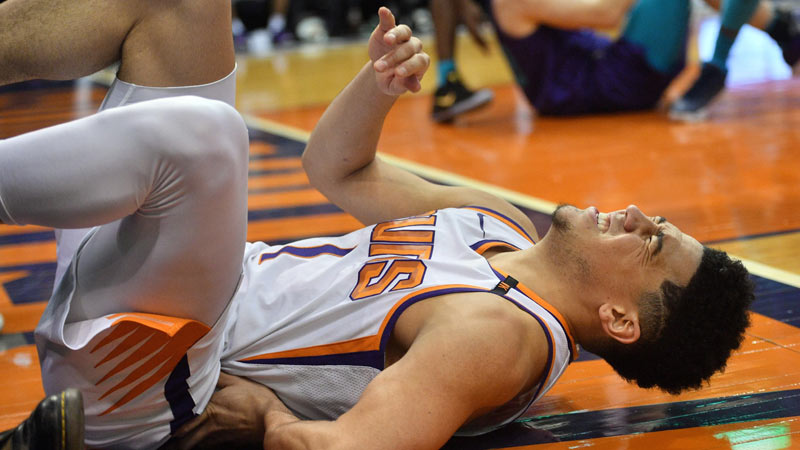

Source: azcentral.com
A hip pointer is a contusion or bruise on the iliac crest, the top of the hip bone. Basketball players may sustain a hip pointer injury from direct blows or collisions during games.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and difficulty with hip movement. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, and protective padding. In severe cases, pain management, physical therapy, and a gradual return to activity may be necessary.
Protective equipment and playing with proper technique can help reduce the risk of hip pointer injuries.
ACL Tear
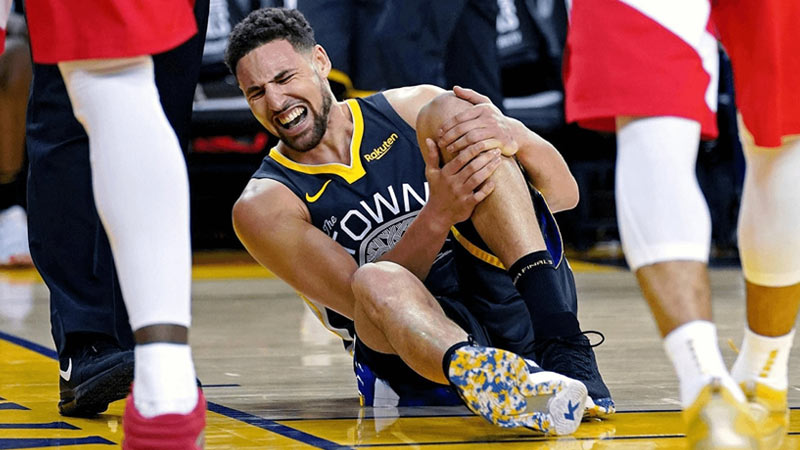

Source: aesmphysiotherapytoronto.ca
An ACL tear is a severe and debilitating knee injury that commonly affects basketball players. It occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament, one of the major ligaments in the knee, is torn or ruptured.
The injury often happens during sudden stops, pivots, or awkward landings, putting excessive stress on the ligament. Players may experience immediate pain, swelling, and instability in the knee.
Treatment for an ACL tear usually involves surgical reconstruction of the ligament using a graft, followed by a comprehensive rehabilitation program. The surgery aims to restore stability to the knee joint and enable players to return to their pre-injury level of activity.
Rehabilitation focuses on strengthening the surrounding muscles, improving flexibility, and gradually reintroducing basketball-specific movements to regain functional mobility and prevent future injuries.
Meniscus Tear
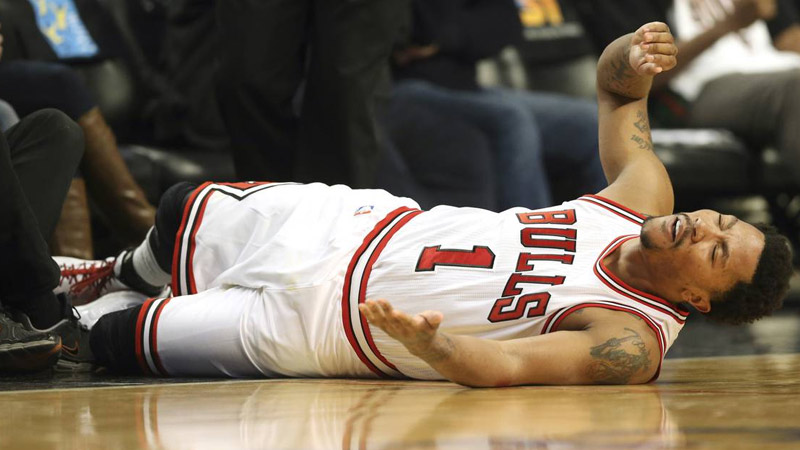

Source: chicagotribune.com
Basketball players are susceptible to meniscus tears, which are injuries to the cartilage in the knee joint. Twisting motions, abrupt changes in direction, and direct impact can cause the meniscus to tear. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited range of motion in the knee.
Treatment for a meniscus tear depends on the location, size, and severity of the tear. In some cases, conservative measures like rest, ice, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medication may be sufficient for healing.
However, more significant tears may require arthroscopic surgery to repair or remove the damaged meniscus.
Dislocated Shoulder
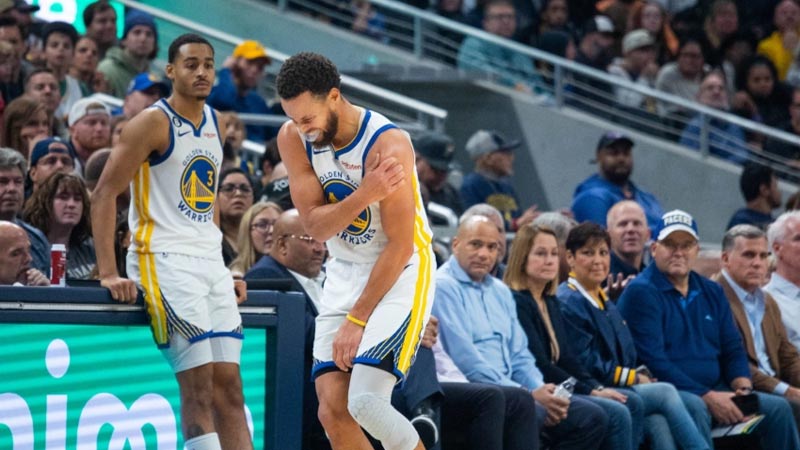

Source: japantimes.co
A dislocated shoulder occurs when the upper arm bone (humerus) pops out of the shoulder socket. Basketball players may experience this injury from collisions, falls, or attempting to break a fall with an outstretched arm. The dislocation causes severe pain, shoulder deformity, and limited mobility.
Immediate medical attention is necessary for a dislocated shoulder to relocate the joint back into place.
Following reduction, rehabilitation focuses on strengthening the muscles around the shoulder, improving stability, and gradually reintroducing sports-specific activities.
In some cases of recurrent shoulder dislocations, surgical intervention may be recommended to repair or stabilize the joint.
Rotator Cuff Tear

Source: abc11.com
The rotator cuff consists of a group of tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and facilitating arm movements. Basketball players are susceptible to rotator cuff tears due to the repetitive overhead motions involved in shooting, passing, and rebounding.
Symptoms of a rotator cuff tear include shoulder pain, weakness, and limited range of motion.
Treatment options for a rotator cuff tear vary depending on the size and severity of the tear. Conservative management, such as physical therapy focused on strengthening the surrounding muscles and improving shoulder mechanics, may be effective for smaller tears.
However, larger tears or cases that do not respond to conservative treatment may require surgical repair of the torn tendons.
Finger Fractures/dislocations

Source: inquirer.com
Finger fractures and dislocations are prevalent injuries in basketball due to the frequent hand contact involved in dribbling, catching, and attempting steals.
When the finger experiences a direct impact or gets caught in an opponent’s jersey or the basketball itself, it can lead to fractures or dislocations. These injuries cause immediate pain, swelling, deformity, and difficulty moving the affected finger.
Treatment typically involves immobilizing the finger with a splint or cast to promote healing and stability. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the bones or repair damaged ligaments.
Wrist Sprain

Source: blackberryclinic.co
Wrist sprains occur when the ligaments that support the wrist joint are overstretched or torn, often as a result of falls or forceful impacts while playing basketball.
This injury is common when players attempt to break their fall using their hands or wrists. Symptoms of a wrist sprain include pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
Treatment involves the RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) method, along with the use of a brace or splint to immobilize the wrist. Physical therapy exercises may be recommended to regain strength and flexibility in the affected wrist.
Concussion

Source: nytimes.com
Concussions are a form of traumatic brain injury that can occur in basketball due to collisions, falls, or head-to-head contact. When a player experiences a blow to the head, the brain can move within the skull, resulting in concussion symptoms.
These symptoms include headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, and sensitivity to light or noise. Immediate rest, both physical and cognitive, is crucial for concussion management.
Gradual return to activity is supervised and follows a stepwise protocol to ensure the player’s safety and full recovery.
Bruised Ribs
Source: medicalnewstoday.com
Basketball players are susceptible to bruised ribs due to the physicality of the game and the potential for collisions.
When the ribs suffer a direct blow or compression, the underlying tissues can become bruised and painful. Symptoms include localized tenderness, pain, and difficulty taking deep breaths.
Treatment primarily focuses on pain management, rest, and avoiding activities that worsen the pain. Gradually returning to normal activities is advised once the pain subsides.
Back Strain

Source: sandiegouniontribune.com
Back strains can occur in basketball due to the repetitive jumping, landing, and sudden twisting motions involved in the sport. These movements can strain the muscles, ligaments, or tendons in the back, leading to pain, stiffness, and muscle spasms.
Treatment for back strains typically involves rest, ice therapy, heat therapy, gentle stretching exercises, and strengthening exercises that target the core and back muscles. Proper body mechanics, warm-up routines, and conditioning can help prevent back strains.
Plantar Fasciitis
Source: bsmpg.com
Plantar fasciitis is an overuse injury characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that connects the heel to the toes.
Basketball players can develop plantar fasciitis due to the repetitive running and jumping involved in the game.
Symptoms include heel pain and stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of rest. Treatment includes rest, ice, stretching exercises, footwear modifications, orthotic inserts, and physical therapy to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve foot biomechanics.
Stress Fractures

Source: emergeortho.com
Stress fractures are small cracks in the bone that develop due to repetitive stress, overuse, or inadequate recovery time. Basketball players, especially those engaged in intense training or playing multiple games, are at risk of stress fractures.
Common sites of stress fractures in basketball include the tibia (shinbone), foot, and lower leg. Rest and reducing the impact on the affected area are crucial in treating stress fractures.
Immobilization with a cast, boot, or crutches may be necessary, and gradually increasing activity levels under medical supervision help ensure proper healing.
Broken Bones

Source: cbsnews.com
Basketball players are susceptible to broken bones, also known as fractures, particularly in areas like the wrists, fingers, ankles, and feet. Falls, collisions, and forceful impacts during the game can lead to fractures.
Symptoms include immediate pain, swelling, deformity, and difficulty moving the affected limb or joint. Treatment depends on the location and severity of the fracture, ranging from immobilization with casts, splints, or braces to surgical intervention for more complex fractures.
Rehabilitation and physical therapy may be necessary to regain strength, range of motion, and functional abilities after bone fractures.
These common basketball injuries highlight the physical demands and potential risks associated with the sport. Prompt medical evaluation, proper treatment, and rehabilitation are essential for a full recovery and safe return to the basketball court.
FAQs
What are the most common basketball injuries?
The most common basketball injuries include ankle sprains, knee sprains, Achilles tendonitis, patellar tendinitis, shin splints, hamstring strains, groin strains, hip pointers, ACL tears, meniscus tears, dislocated shoulders, rotator cuff tears, finger fractures/dislocations, wrist sprains, concussions, bruised ribs, back strains, plantar fasciitis, stress fractures, and broken bones.
How can ankle sprains be prevented in basketball?
Ankle sprains can be prevented by wearing supportive basketball shoes, using ankle braces or taping for additional stability, practicing proper landing techniques, and participating in ankle-strengthening exercises and balance training.
What is the treatment for patellar tendinitis?
The treatment for patellar tendinitis includes rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE therapy), physical therapy exercises to strengthen the quadriceps and hamstrings, stretching, anti-inflammatory medication, and the use of patellar straps or knee sleeves for support.
How long does it take to recover from an ACL tear?
The recovery time for an ACL tear varies depending on the severity of the injury, individual factors, and the chosen treatment approach. Generally, recovery can take anywhere from several months to a year, involving rehabilitation exercises, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgical reconstruction.
Can stress fractures be prevented in basketball?
To help prevent stress fractures in basketball, it is important to gradually increase training intensity, wear appropriate footwear with good shock absorption, maintain proper nutrition and hydration, and incorporate cross-training activities that reduce the repetitive impact on the lower body.
Conclusion
Basketball is a sport that demands physicality, agility, and athleticism, making it prone to a variety of injuries. From common sprains and strains to more severe ligament tears and fractures, basketball players should be aware of the potential risks associated with the game.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these common basketball injuries, players can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of injury and seek appropriate medical care when needed.
Also, helps focus on preventive measures and proper rehabilitation to stay on the court and enjoy the game they love.
Remember, safety and well-being should always be a priority to ensure a long and successful basketball career.







